HOW DO I MANAGE MY VM?
Let's see first the many states of your VMs. Each VM can be in one of 3 states:
Running: The VM is working properly and you can connect to it.
Stopped: The VM is switched off.
Rebooting: The VM restarts, it will soon be Running and you will be able to use it.
Also, you can see the IPv4 and IPv6 address of each VM. Finally, with "Info" you can see some technical features of the machine, such as number of core CPUs, RAM size, Image size, CPU and network usage and link to the VM's tag edit page.
Pointing the mouse over the VM you want to manage will show this menu, if the VM is running:
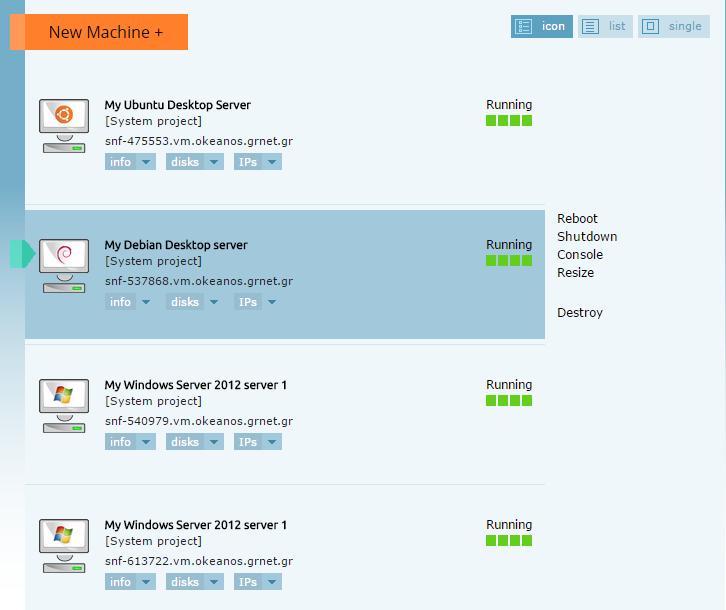
The available options are the following:
- Reboot: Restart the VM
- Shutdown: Shut down the VM
- Console: Access to the virtual machine via Java without using a remote connection program. This is used primarily for troubleshooting.
- Resize: Modify the technical specifications of your VM.
- Destroy: Destruction of the VM! Irreversible process!
Otherwise, if it is stopped, you should see the following menu:
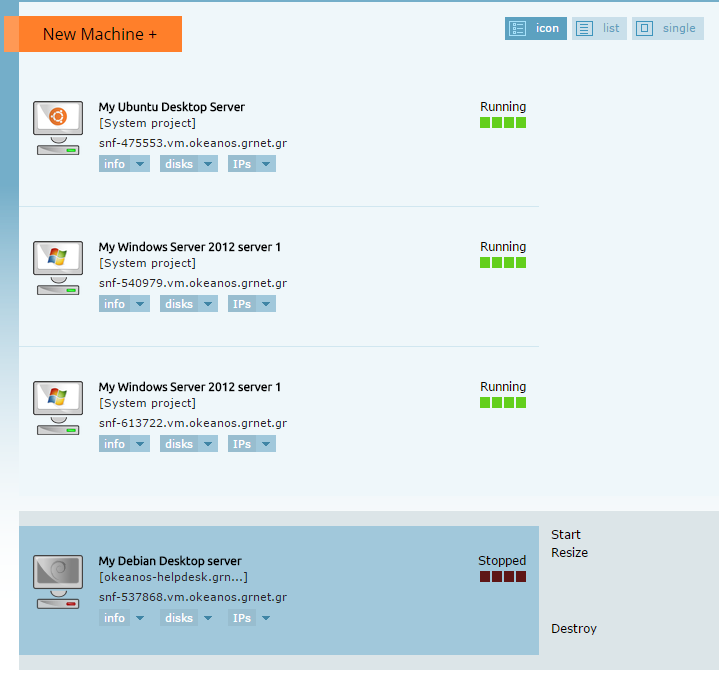
The available options are:
- Start: Start the VM
- Resize: Modify the technical specifications of your VM.
- Destroy: Destruction of the VM! (Yes yes, irreversible process ...)
CYCLADES USER GUIDE
- How to create a VM?
- How do I connect to a VM?
- How do I manage my VM?
- How can I resize the CPU/RAM of an existing VM?
- How can I attach/detach an IP on a running VM?
- How can I add extra disks to my VMs?
- How can I detach an extra disk from a VM?
- How can I add tags to my VMs?
- How can I assign my VM to a project?
- What are SSH keys and how can I use them?
- What are private networks?
- What is a firewall and which one should I choose?
- How to create VMs from custom images?
- How can I access all my VMs using one public IP (NAT)?
- How can I update the VirtIO drivers of my Windows VM?
- How can I add IPv6 nameservers on my CentOS/Oracle Linux VM?



